Global Anti-Money Laundering (GAML): An Inclusive Dictionary Guide
Global Anti-Money Laundering (GAML) is a comprehensive framework and set of regulations aimed at preventing and detecting money laundering and terrorist financing activities on a global scale. It involves the implementation of various measures, including customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, reporting obligations, and the establishment of robust compliance frameworks. GAML seeks to safeguard the integrity of the global financial system and combat illicit financial activities that can have serious economic and security implications.
 Written by Erling Andersen
Written by Erling Andersen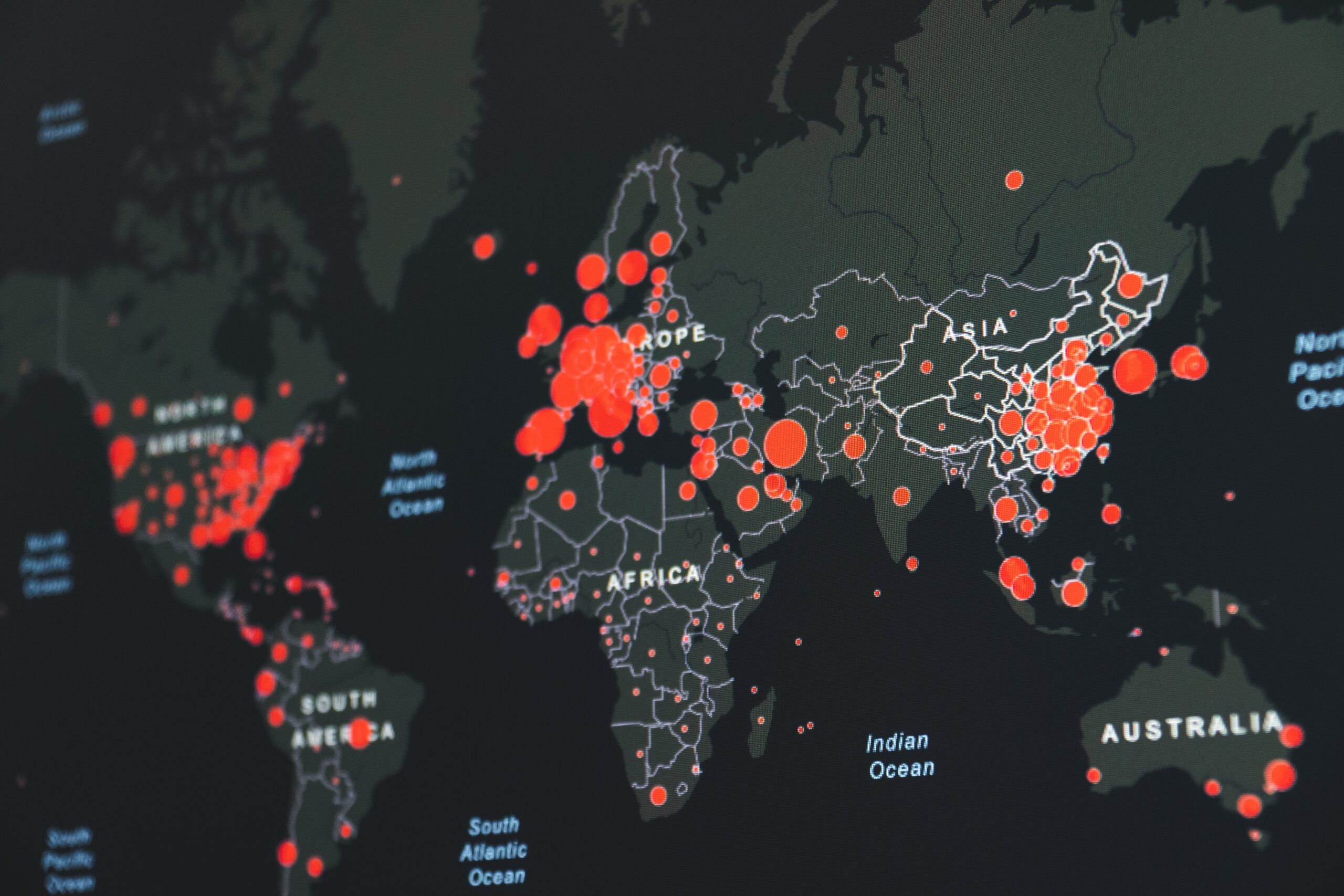
Welcome to our comprehensive dictionary article on Global Anti-Money Laundering (GAML). This article will provide AML professionals with a detailed definition, practical examples, statistics, and insights into the world of GAML. We will also introduce the Kyros AML Data Suite, a powerful AML compliance SaaS software designed to enhance your GAML efforts.
Definition:
Global Anti-Money Laundering (GAML) refers to the collective efforts and initiatives undertaken globally to combat money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit financial activities. It involves the implementation of comprehensive AML frameworks, regulations, and measures by governments, regulatory authorities, and financial institutions to prevent, detect, and deter money laundering on a global scale.
Practical Examples:
Now, we explore the practical examples and key concepts of this crucial field. Global Anti-Money Laundering refers to the collective efforts, regulations, and measures implemented by countries worldwide to combat the illegal flow of funds through financial systems. This guide aims to provide AML professionals with a deeper understanding of the practical applications and implications of GAML. From customer due diligence to transaction monitoring, we will delve into various aspects of GAML, shedding light on its significance in preventing money laundering and terrorist financing activities. Join us on this informative journey to enhance your knowledge and stay up-to-date with the evolving landscape of global AML regulations.
International Cooperation:
International cooperation is a vital aspect of Global Anti-Money Laundering (GAML) efforts. With the increasing globalization of financial transactions, it has become imperative for countries to collaborate and share information to combat money laundering effectively. International cooperation involves the exchange of intelligence, sharing of best practices, and coordination among financial intelligence units (FIUs) and law enforcement agencies across different jurisdictions.
This collaboration enables the identification and disruption of cross-border money laundering networks, making it harder for criminals to exploit global financial systems. Through mechanisms such as mutual legal assistance treaties (MLATs) and international organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), countries work together to develop common standards, conduct joint investigations, and provide support in prosecuting money laundering and related crimes. By fostering international cooperation, GAML aims to create a unified global front against money laundering, ultimately safeguarding the integrity of the global financial system.
Know Your Customer (KYC):
Know Your Customer (KYC) is a fundamental principle of Global Anti-Money Laundering (GAML) efforts. It refers to the process by which financial institutions and other regulated entities verify the identity of their customers and assess their risk profiles. KYC procedures involve collecting and verifying relevant information such as identification documents, proof of address, and beneficial ownership details.
By implementing robust KYC measures, GAML aims to prevent the use of financial systems for illicit purposes and detect potential money laundering activities. KYC helps financial institutions establish the true identity of their customers, understand their business activities, and assess the potential risk of money laundering or terrorist financing. It enables the identification of politically exposed persons (PEPs) and individuals or entities with a higher risk profile, ensuring enhanced due diligence measures are applied. KYC requirements vary across jurisdictions but generally involve customer identification, risk assessment, ongoing monitoring, and record-keeping. By adhering to KYC practices, GAML seeks to create a more transparent and accountable financial system, mitigating the risk of money laundering and protecting the integrity of the global economy.
Transaction Monitoring:
Transaction Monitoring is a vital component of Global Anti-Money Laundering (GAML) efforts, aimed at detecting and reporting suspicious financial activities. It involves the systematic review and analysis of customer transactions to identify any unusual or suspicious patterns that may indicate money laundering or other illicit activities. Transaction monitoring systems use advanced algorithms and technologies to analyze large volumes of data in real-time, looking for red flags such as high-value transactions, frequent cash deposits or withdrawals, structuring of transactions to avoid reporting requirements, and transactions involving high-risk jurisdictions or individuals.
By continuously monitoring transactions, financial institutions can identify and investigate suspicious activities, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and preventing money laundering and terrorist financing. Transaction monitoring is not only essential for detecting suspicious activities but also for creating a comprehensive record of financial transactions, which can be invaluable during regulatory audits and investigations. It helps financial institutions maintain a robust compliance framework and contributes to the overall effectiveness of GAML efforts by mitigating the risk of illicit financial activities and preserving the integrity of the global financial system.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD):
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is a crucial tool in the Global Anti-Money Laundering (GAML) framework, designed to mitigate the risks associated with higher-risk customers or business relationships. EDD goes beyond the standard due diligence procedures and involves a more in-depth investigation and analysis of the customer’s background, activities, and sources of funds. It is typically applied to customers who pose a higher inherent risk, such as politically exposed persons (PEPs), high-net-worth individuals, or customers from high-risk jurisdictions.
EDD requires financial institutions to gather additional information and documentation, conduct thorough risk assessments, and apply enhanced monitoring measures. This may include verifying the customer’s identity through multiple reliable sources, scrutinizing the customer’s business relationships and affiliations, assessing the purpose and expected nature of the business relationship, and understanding the source of the customer’s wealth.
By conducting EDD, financial institutions can gain a deeper understanding of their customers and identify any potential red flags or vulnerabilities that may expose them to money laundering or terrorist financing risks. EDD helps to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, safeguard the institution’s reputation, and mitigate the risk of being involved in illicit activities.
Implementing robust EDD processes and systems is essential for detecting and preventing money laundering and other financial crimes. It enables financial institutions to make informed decisions about customer relationships, allocate resources effectively, and develop risk-based mitigation strategies. By conducting thorough EDD, financial institutions contribute to the overall effectiveness of GAML efforts, strengthening the integrity of the global financial system and promoting a safer and more transparent business environment.
Regulatory Reporting:
Regulatory Reporting plays a vital role in the Global Anti-Money Laundering (GAML) framework, ensuring that financial institutions comply with the reporting obligations imposed by regulatory authorities. It involves the timely and accurate submission of various reports and disclosures related to anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) activities.
Financial institutions are required to report suspicious transactions, large cash transactions, and other relevant information to the appropriate regulatory bodies. These reports provide valuable insights into potential money laundering or terrorist financing activities and aid in the identification of trends, patterns, and emerging risks.
Regulatory reporting serves multiple purposes. First and foremost, it allows regulatory authorities to monitor and assess the effectiveness of AML and CTF measures implemented by financial institutions. It helps detect and prevent financial crimes, identify vulnerabilities in the system, and take necessary actions to protect the integrity of the financial sector.
Additionally, regulatory reporting enhances transparency and accountability within the industry. It fosters trust among stakeholders, as it demonstrates that financial institutions are actively fulfilling their legal and regulatory obligations to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
To ensure accurate and timely regulatory reporting, financial institutions must establish robust systems and processes. These include implementing advanced transaction monitoring systems, maintaining comprehensive records, and conducting regular internal audits to assess the effectiveness of their reporting procedures. Automation and technology solutions, such as the Kyros AML Data Suite, can streamline the reporting process, improve data accuracy, and facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements.
By adhering to rigorous regulatory reporting standards, financial institutions contribute to the broader GAML objectives of maintaining the integrity of the global financial system, protecting it from illicit activities, and preserving trust in the industry.
Risk-Based Approach:
The Risk-Based Approach (RBA) is a fundamental principle of the Global Anti-Money Laundering (GAML) framework, providing a practical and effective strategy for combating money laundering and terrorist financing. In this approach, financial institutions assess and manage the risks associated with their customers, products, services, and geographic locations to allocate their resources and implement appropriate measures.
By adopting a risk-based approach, financial institutions can focus their efforts on areas that pose a higher risk of money laundering or terrorist financing, thereby optimizing their resources and enhancing the effectiveness of their anti-money laundering (AML) efforts. This approach recognizes that not all customers or transactions carry the same level of risk, and therefore, different levels of due diligence and control measures are required.
Financial institutions employ a range of risk assessment tools and techniques to determine the risk profiles of their customers and activities. These include customer due diligence (CDD), enhanced due diligence (EDD), transaction monitoring, and ongoing monitoring. The risk assessment process involves analyzing various factors such as customer characteristics, transaction patterns, geographic locations, and industry sectors to assign risk ratings and determine the appropriate level of scrutiny.
By tailoring their AML measures based on risk, financial institutions can allocate their resources more efficiently and effectively. High-risk customers or activities warrant more stringent due diligence procedures and ongoing monitoring, while low-risk entities may receive simplified procedures, allowing for a smoother customer experience without compromising the overall risk management objectives.
The risk-based approach is not only a regulatory requirement but also a best practice that promotes a more targeted and efficient approach to combating money laundering and terrorist financing. It allows financial institutions to adapt to evolving risks, prioritize their efforts, and allocate resources based on the level of risk. The use of advanced technology and data analytics, such as the Kyros AML Data Suite, can further enhance the risk-based approach by providing real-time insights and automated risk assessment capabilities.
Statistics and Relevant Numbers:
Global Anti-Money Laundering (GAML) efforts have gained significant momentum in recent years, driven by the need to combat the growing threats posed by money laundering and terrorist financing. The statistics and relevant numbers surrounding GAML highlight the scale of the problem and the importance of implementing robust AML measures.
According to a report by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), it is estimated that between 2% and 5% of global GDP, or roughly $800 billion to $2 trillion, is laundered annually. This staggering amount underscores the magnitude of the issue and the need for coordinated international efforts to tackle money laundering effectively.
Furthermore, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an intergovernmental body that sets international standards for combating money laundering, reports that only a small percentage of global money laundering transactions are detected and intercepted. This highlights the urgency of implementing comprehensive AML frameworks, such as GAML, to enhance detection and prevention measures.
In recent years, there has been an increase in regulatory actions and penalties related to AML violations. Financial institutions have faced significant fines and reputational damage for failing to meet their AML obligations. For example, in 2020, global banks paid over $10 billion in fines for AML-related violations, emphasizing the strict enforcement measures being taken to combat money laundering.
These statistics highlight the critical role of GAML in addressing the global money laundering problem. The adoption of robust AML frameworks, such as the risk-based approach, transaction monitoring, and customer due diligence, is crucial for financial institutions to mitigate the risks associated with money laundering and terrorist financing.
Benefits of the Kyros AML Data Suite:
The Kyros AML Data Suite offers numerous benefits for Global Anti-Money Laundering (GAML) efforts, empowering financial institutions and AML professionals to enhance their compliance measures and mitigate the risks associated with money laundering and terrorist financing.
One of the key benefits of the Kyros AML Data Suite is its advanced data analytics capabilities. The software leverages sophisticated algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze vast amounts of data in real time. This enables financial institutions to identify patterns, detect suspicious activities, and uncover hidden connections that may indicate money laundering or illicit transactions. By leveraging the power of data analytics, the Kyros AML Data Suite significantly enhances the effectiveness of transaction monitoring and risk assessment processes.
Another crucial benefit is the automation of compliance processes. The Kyros AML Data Suite streamlines and automates various AML tasks, such as customer due diligence, enhanced due diligence, and regulatory reporting. This not only saves time and resources but also reduces the risk of human error, ensuring consistent and accurate compliance across the organization. The automation features of the Kyros AML Data Suite enable financial institutions to improve operational efficiency and focus their efforts on high-risk areas that require human expertise.
Furthermore, the Kyros AML Data Suite offers enhanced risk assessment capabilities. By integrating multiple data sources and applying advanced risk models, the software enables financial institutions to assess the risk associated with customers, transactions, and counterparties more accurately. This helps in identifying and prioritizing high-risk entities, allowing organizations to allocate resources effectively and take appropriate risk mitigation measures.
Additionally, the Kyros AML Data Suite provides a comprehensive audit trail and reporting functionalities. It generates detailed reports and documentation, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and facilitating internal and external audits. The software also assists in regulatory reporting, helping financial institutions meet their reporting obligations promptly and accurately.
Conclusion:
As AML professionals, staying abreast of the evolving GAML landscape is crucial. By adopting a comprehensive GAML framework and leveraging innovative solutions like the Kyros AML Data Suite, organizations can strengthen their AML compliance efforts, combat money laundering, and contribute to a safer financial ecosystem. To learn more about the Kyros AML Data Suite and its benefits for your GAML initiatives, visit kyrosaml.com.
Share article on
